Mass-personalized or -customized products at near mass-production prices is a huge potential area for growth for digital print. Only with digital can you print in real time onto anything and everything, such as 3D objects, clothing, flooring, tiles and wallcoverings, to give a unique customized product.
In this post, Martin Bailey, former CTO and now consultant at Global Graphics Software, explores the rise of the use of variable data and how digital inkjet is the key to unlocking the Holy Grail for many retailers: mass customization at near mass-production prices.
It’s common to think of variable data printing, where at least some of every instance is different from every other instance, as being the preserve of transactional and direct mail printing. Admittedly, that’s where much of it started, but in the broadest sense of the term, variable data printing is now used far more widely, across multiple industries. In situations where the delivery of the product is through a push model (where there is no direct connection between each item produced and a specific recipient at the time of production) several cases are common. Most of these cases are in B2B environments, where the buyer then sells or delivers the result, often B2C.
In mainstream commercial print, labels, packaging and industrial manufacturing, it’s difficult to imagine an alternative to the push model, even given the huge amount of metadata that some companies, such as luxury goods brands and supermarkets, are collecting on their customers.
But there are many situations where there’s a much closer relationship between an end user of the product and the organization that printed or manufactured it, which can be described as a pull model instead. Many of these cases move beyond the traditional idea of variable data as being text and barcodes imaged on top of a static background to each piece being truly unique. They deserve to be described as mass customization, and all of them have been enabled by web-to-print or other forms of online ordering.
The wide format market has long provided display and soft signage, sportswear, tee shirts and car wraps to custom designs on very short runs, down to a single copy. Both signage and sportswear are aimed at both B2B and B2C markets.
Photofinishing has long been a B2C business and has used digital printing for decades. The industry has learned that simply producing 5” x 7” prints does not generate significant profits, but has grown first into photobooks, and then into many other forms of product decoration, printing photographs on hats, shoes, apparel, bed linen, mugs etc and converging with what have historically been wide format opportunities. Each individual order, perhaps for one mug with a photo printed on it, may not appear to be variable data printing. But when orders are aggregated at the producer there may be hundreds or thousands of mugs to be printed per day, each with a different image.

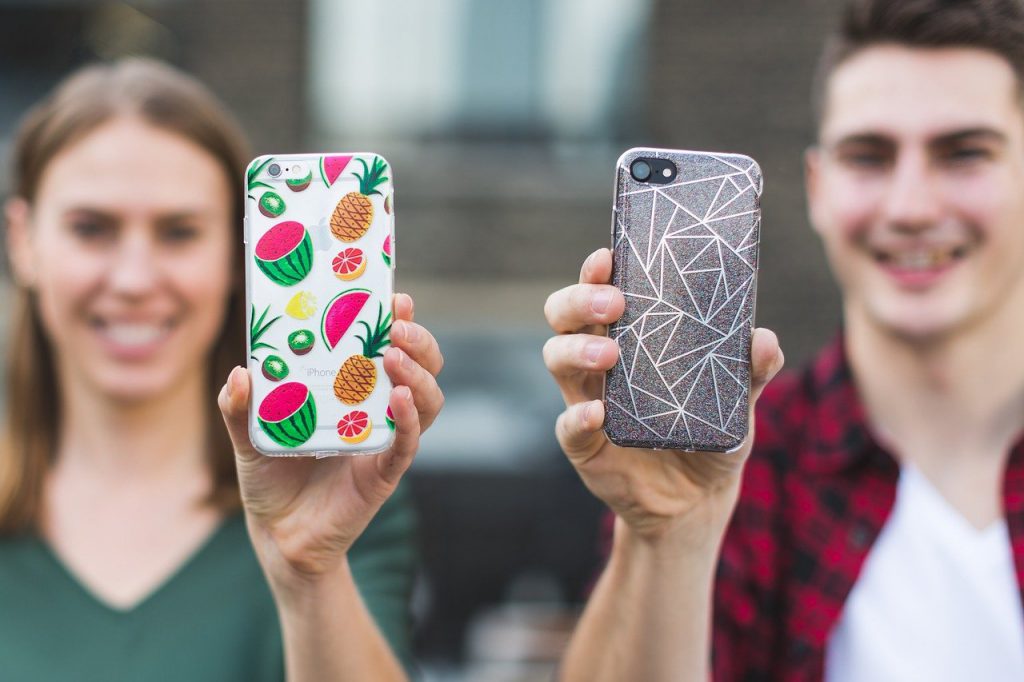
The same business model is applied more broadly to print designs which may be uploaded by the customer and/or created in a web portal by combining the customer’s text and graphics from a library. Examples include phone cases, tee shirts, postcards and greetings cards.
And a number of providers effectively act as publishers for customer designs, managing printing and fulfilment for a variety of products or lengths of custom-printed textile. Examples include Red Bubble and Spoonflower.
Several brands have run campaigns whereby products can be ordered with a name on them, usually for gifting. Examples include “My Nutella” and “My Marmite”. A variant of this is where only a label is purchased, often for bottles of spirits, to be applied to the product by the purchaser themselves.
The most famous campaign for ‘personalized’ labels was Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke”, but in practice most labels were printed in long runs, randomizing the most common names in each country; only labels from roadshows and purchases from the web were actually printed on demand for specific recipients. This makes it an excellent example of a hybrid model taking advantage of the benefits of multiple print technologies.

Even in industries producing a design that would historically have been created in multiple mile or kilometer lengths, such as wallcoverings, there are opportunities for increased margins in custom delivery. As an example, consider a decorating company that has been contracted to apply wallcoverings to a large office. If a wallcovering vendor could deliver pre-cut drops of the wallcovering, each of exactly the right length, and with the pattern starting in exactly the right place so that each drop aligns with those on either side, that would save the decorating company a lot of time. And that, in turn, would allow the vendor to charge a sufficient premium to more than cover the reduced total length required because there is no longer any wastage from the decorators cutting each drop to ensure alignment.
A lot of the demand for this mass customization is ascribed to the changing attitudes and communication preferences of millennials and Gen-Z. To generalize, it’s often said that such audiences demand to be treated, and be able to represent themselves as unique, requiring them to be able to obtain unique product in support of that position.
But the demand is not specific to any age group, according to “The Deloitte Consumer Review – Made-to-order: The rise of mass personalization”, based on survey results from YouGov, which also went on to say: “1 in 5 consumers who expressed an interest in personalized products or services are willing to pay a 20% premium”; that figure rises to around 1 in 2 for customized clothing, furniture, homeware and DIY.

Of course, personalized and customized products are not warehoused at all; they’ve been created for a specific recipient and will usually be shipped immediately.
Inkjet can achieve unique results
Taking short runs to the extreme, a significant advantage for inkjet that applies across the majority of industries is that it does not need to simply reproduce the same invariant design repeatedly, even for a short run; instead, it can make every item different.
Inkjet can achieve unique results in a variety of different industries and being unique in a useful way is a very effective lever for premium pricing and increased profitability.
This is an excerpt from the white paper: Software considerations for inkjet in the smart factory
DOWNLOAD YOUR COPY OF THE WHITE PAPER

Further reading:
What you need to build a press that must handle variable data jobs at high speed
Watch the video: Connecting print to a Smart Factory:
To be the first to receive our blog posts, news updates and product news why not subscribe to our monthly newsletter? Subscribe here
Follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter
1https://www.marmite.co.uk/products/shop/marmite-personalised-classic-jar.html